- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Comparative Study of Ex Vivo Antiplatelet Activity of Aspirin and Cilostazol in Patients with Diabetes and High Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
-
Sangmo Hong, Woo Je Lee, Cheol-Young Park
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):233-242. Published online April 6, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1353
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The role of aspirin in primary cardiovascular disease prevention in patients with diabetes remains controversial. However, some studies have suggested beneficial effects of cilostazol on cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. We prospectively investigated the antiplatelet effects of cilostazol compared with aspirin in patients with diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods
We randomly assigned 116 patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors but no evident cardiovascular disease to receive aspirin at a dose of 100 mg or cilostazol at a dose of 200 mg daily for 14 days. The primary efficacy outcome was antiplatelet effects of aspirin and cilostazol assessed with the VerifyNow system (aspirin response units [ARU]) and PFA-100 (closure time [CT]). Secondary outcomes were changes of clinical laboratory data (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02933788).
Results
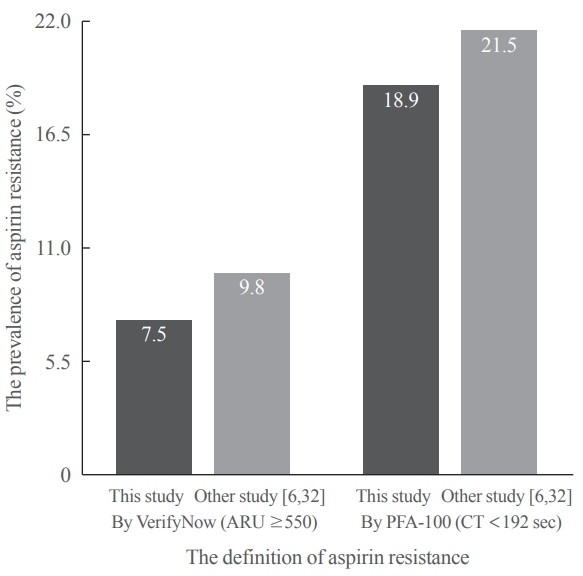
After 14 days, there was greater decrease in ARU in aspirin (–28.9%±9.9%) compared cilostazol (–0.4%±7.1%, P<0.001) and was greater increase in CT in aspirin (99.6%±63.5%) compared cilostazol (25.7%±54.1%, P<0.001). The prevalence of aspirin resistance was 7.5% according to VerifyNow (defined by ARU ≥550) and 18.9% according to PFA-100 (CT <192 seconds). Compared with aspirin, cilostazol treatment was associated with increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (7.1%±12.7% vs. 4.2%±18.0%, P=0.006) and decreased triglycerides (–9.4%±33.7% vs. 4.4%±17.57%, P=0.016). However, there were no significant changes in total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol, C-reactive protein level, and cluster of differentiation 40 ligand between cilostazol and aspirin groups.
Conclusion
Aspirin showed better antiplatelet effects assessed with VerifyNow and PFA-100 compared with cilostazol. However, there were favorable changes in atherogenic dyslipidemia only in the cilostazol.
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Prognostic Value of Triglyceride and Glucose Index for Incident Type 2 Diabetes beyond Metabolic Health and Obesity
-
Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Chang Hee Jung
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1042-1054. Published online October 21, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1184
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Metabolically healthy obese (MHO) phenotype is metabolically heterogeneous in terms of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Previously, the triglyceride and glucose (TyG) index has been considered for identifying metabolic health and future risk of T2D. This study aimed to evaluate the risk of incident T2D according to obesity status and metabolic health, categorized by four different criteria and the TyG index.
Methods
The study included 39,418 Koreans without T2D at baseline. The risk of T2D was evaluated based on four different definitions of metabolic health and obesity status and according to the baseline TyG index within each metabolic health and obesity group.
Results
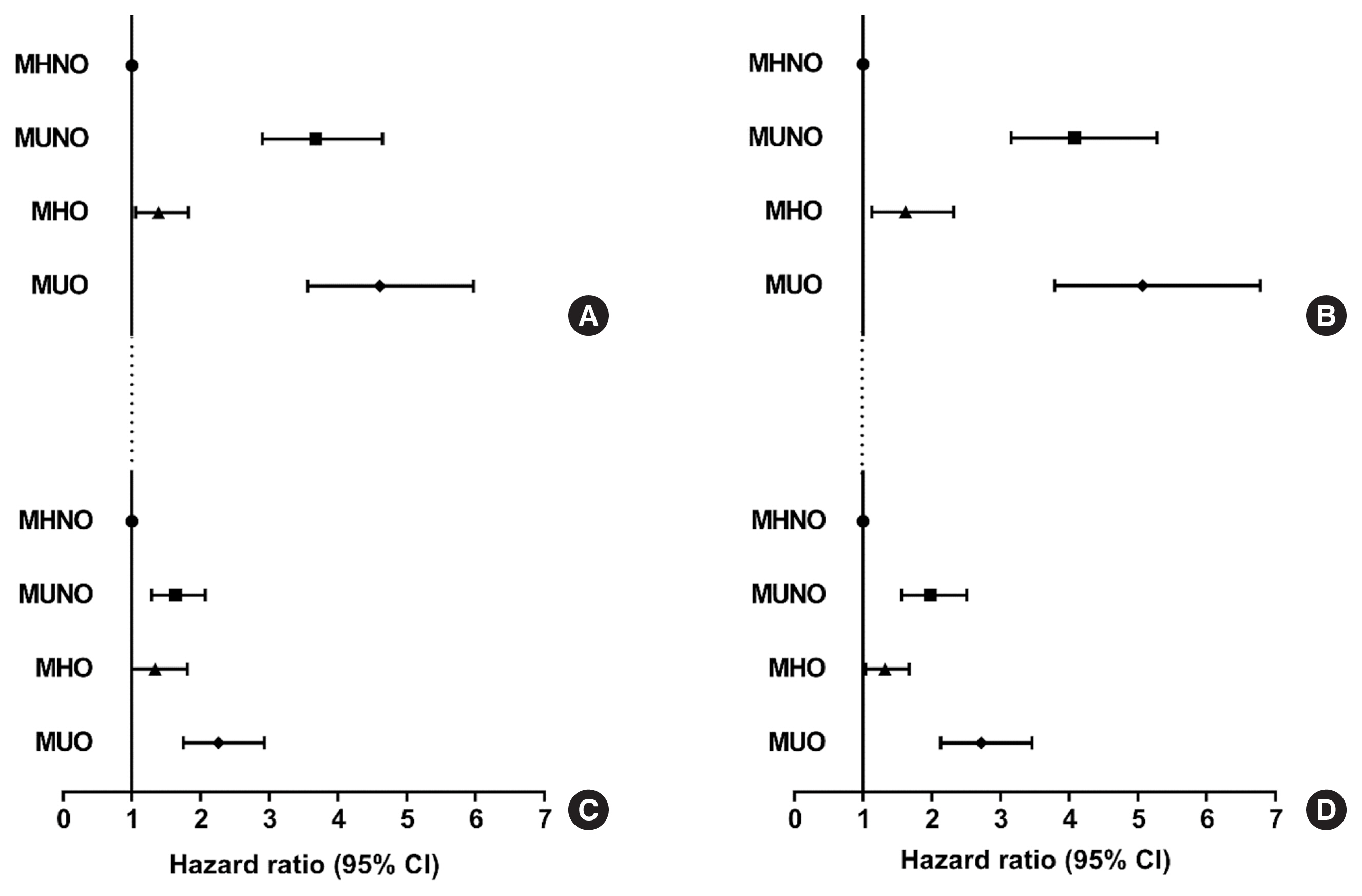
During the median follow-up at 38.1 months, 726 individuals developed T2D. Compared with the metabolically healthy non-obese (MHNO) group with low TyG index, the MHO group with high TyG index showed increased risk of T2D in all four definitions of metabolic health with multivariate-adjusted hazard ratios of 2.57 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.76 to 3.75), 3.72 (95% CI, 2.15 to 6.43), 4.13 (95% CI, 2.67 to 6.38), and 3.05 (95% CI, 2.24 to 4.15), when defined by Adult Treatment Panel III, Wildman, Karelis, and homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) criteria, respectively.
Conclusion
MHO subjects with high TyG index were at an increased risk of developing T2D compared with MHNO subjects, regardless of the definition of metabolic health. TyG index may serve as an additional factor for predicting the individual risk of incident T2D in MHO subjects.
- A Case of Malignant Pheochromocytoma Presenting as Inverted Takotsubo-Like Cardiomyopathy.
-
Jung Eun Jang, Hyuk Hee Kwon, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Sung Jin Bae, Hong Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):98-104. Published online March 1, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.98
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy or stress induced cardiomyopathy is characterized by acute transient left ventricular apical ballooning without significant coronary artery disease. The pathophysiology of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy remains unclear, but it has been suggested that the stress related neurohumoral factors, especially catecholamines, play an important role. Recently, several reports have described an inverted Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, which is characterized by the dysfunction of the basal and mid-ventricular segments sparing the apex of the heart. In this report, we present a case of a 50-year-old female with a transient left ventricular dysfunction in an inverted Takotsubo pattern, that later was diagnosed as a malignant pheochromocytoma.
- A Case of Familial Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 with a Novel Mutation in the MEN1 Gene.
-
Min Jung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Mi Seon Shin, Joo Hui Kim, Hee Kyung Na, Seong Joon Park, Sang Ah Lee, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Ki Ho Song, Joong Yeol Park, Ki Up Lee, Gu Hwan Kim, Han Wook Yoo, Min Seon Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(2):171-176. Published online June 1, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.2.171
-
-
1,955
View
-
31
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the occurrence of multiple tumors in the parathyroid gland, pancreatic islet, and pituitary gland. This condition is caused by mutations of MEN1, a tumor suppressor gene. Thus far, 565 different germline and somatic mutations of the MEN1 gene have been reported. Herein, we describe the case of a 23-year-old woman who suffered from a repetitive loss of consciousness. After workup, the patient was diagnosed with MEN1 with insulinoma, hyperparathyrodism due to parathyroid adenoma, and non-functioning pituitary microadenoma. She underwent a partial parathyroidectomy and distal pancreatectomy. Familial screening of MEN1 revealed that her brother had prolactinoma, hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic gastrinoma and non-functioning adrenal adenoma. Her father had hyperparathyroidism, pancreatic tumor, and adrenal adenoma. Upon genetic analysis of the MEN1 gene, a novel mutation in the MEN1 gene (exon 1, c.251del; p.Ser84LuefsX35) was detected in the patient, as well as her father and brother.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Parathyroid disorder and concomitant thyroid cancer in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
Ying Wang, Sheng Cai, He Liu, Rui-Na Zhao, Xing-Jian Lai, Ke Lv, Yu-Xin Jiang, Jian-Chu Li
Medicine.2021; 100(36): e27098. CrossRef - Genetic and Epigenetic Analysis in Korean Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1
Yoon Jung Chung, Sena Hwang, Jong Ju Jeong, Sun Yong Song, Se Hoon Kim, Yumie Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 270. CrossRef
- Brown Tumor of the Ulna and Radius: An Unusual Presentation of Primary Hyperparathyroidism.
-
Hyun Park, Gun Hi Kang, Seung Gu Kim, Jun Jae Kim, Na Na Baek, Dae Myung Kim, Sung Woo Cho, Woo Je Lee, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(5):347-351. Published online October 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.5.347
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Brown tumors are erosive bony lesions caused by chronic excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone. Since the introduction of routine calcium measurement, the diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism has usually been made in asymptomatic patients and as a result, brown tumors are rarely observed as an initial manifestation of hyperparathyroidism.
- Intensive Glucose Control and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Focused on Recent Clinical Trials.
-
Woo Je Lee, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(5):289-297. Published online October 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.5.289
-
-
1,571
View
-
17
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Influence of Admission Hypoglycemia on Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Jung Kim, Myung Ho Jeong, In Seok Jeong, Sang Gi Oh, Sang Hyung Kim, Young keun Ahn, Ju Han Kim, Young Jo Kim, Shung Chull Chae, Taek Jong Hong, In Whan Seong, Jei Keon Chae, Chong Jin Kim, Myeong Chan Cho, Ki Bae Seung, Hyo Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Medicine.2014; 87(5): 565. CrossRef
- A Case of Acute Pancreatitis and Severe Hypertriglyceridemia Associated with Clozapine.
-
Hye Kyeong Park, Hye Jin Won, Hyo Seung Ahn, Ban Suk Lee, Seung Gu Kim, Woo Je Lee, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(5):381-385. Published online October 1, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.5.381
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Clozapine, an atypical antipsychotic agent, has been linked to several cases of acute pancreatitis and hypertriglyceridemia. However, neither acute pancreatitis nor hypertriglyceridemia associated with clozapine has yet been reported in the Republic of Korea. Based on recent experience, we report on a case of severe hypertriglyceridemia and acute pancreatitis associated with clozapine. A 37-year-old schizophrenic woman in good physical condition presented with abdominal pain of acute onset. She had been taking clozapine for 20 months to control her schizophrenia. On admission, her serum triglyceride level was 6,670 mg/dL. Elevated serum amylase and lipase levels, as well as abdominal computed tomography findings, were compatible with acute pancreatitis. After discontinuing the use of clozapine, the serum triglyceride level was normalized and acute pancreatitis resolved.
- A Case of Hyperthyroidism Associated with Symptomatic Hypercalcemia.
-
Ju Hyun Choi, Woo Je Lee, Yun Hee Chung, Hye Won Park, Dan Bi Lee, Jong Chul Won, Duk Jae Kim, Ghi Su Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(3):251-256. Published online June 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.3.251
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Two of the common causes of hypercalcemia are malignancy and primary hyperparathyroidism. These disorders are easily diagnosed by the clinical manifestations and measurement of the serum intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) level. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism is an uncommon cause of hypercalcemia. The diagnosis of hypercalcemia associated with hyperthyroidism can only be made by excluding the common causes of hypercalcemia and by observing the improvement of the hypercalcemia and its associated symptoms with normalizing the thyroid function. Herein we reported our experience with a 67 year-old woman who presented with nausea and vomiting. She showed elevated serum calcium and phosphorus levels. Serum intact PTH level was 1.1 pg/mL (normal range; 10~65). The results of the thyroid function test were compatible with hyperthyroidism. After resolution of the thyrotoxicosis with combination treatment of methimazol and Lugol's solution, the patient's serum calcium and phosphorus levels were normalized and the symptoms were improved.
- Improvement of Metabolic Syndrom by Alpha-lipoic Acid.
-
Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min Seon Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Ki Up Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(3):267-273. Published online June 1, 2004
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
|